Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
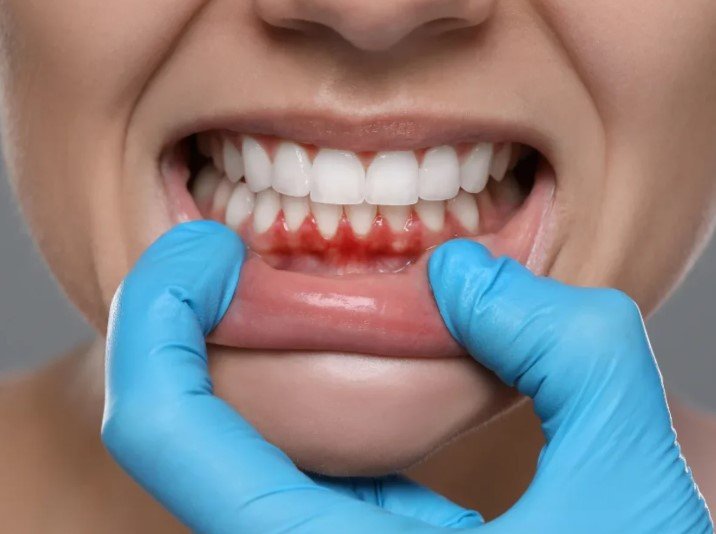
Understanding the options for receding gums treatment at home vs dentist cost is essential for millions of adults facing this common dental problem. This guide explains gum recession, explores the full spectrum of treatments from home care to advanced surgical procedures, and provides clear cost comparisons to help you make an informed decision. The core difference lies in efficacy and long-term outcome: while home strategies focus on prevention and halting mild recession, professional dental treatments are necessary to repair existing damage, restore gum tissue, and protect your oral health from further decline.
Knowing your options for receding gums treatment provides three main benefits. First, it empowers you to take early, effective action to prevent tooth loss and sensitivity. Second, it allows for realistic financial planning by comparing the minimal cost of home care with the investment in professional procedures like gum graft surgery or the Pinhole Surgical Technique. Third, it highlights the value of professional diagnosis, ensuring you receive the correct treatment—whether it’s a simple professional deep cleaning or a more complex surgical intervention—for your specific stage of gingival recession.
This knowledge applies to several key decisions. It helps you determine when at-home remedies like improved oral hygiene are sufficient versus when you need to seek gum recession treatment from a dental professional. It assists in evaluating treatment options based on severity, from non-surgical treatments for early stages to surgical options for advanced cases. Ultimately, it guides you in investing in long-term oral health, preventing the higher costs and complications of untreated periodontal disease.
The comparison between receding gums treatment at home vs dentist cost consists of four main components. The first is home care and natural remedies, which includes proper brushing technique with a soft-bristled toothbrush, antimicrobial rinses, and lifestyle changes. The second is non-surgical professional treatments, such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning). The third is surgical solutions, including gum graft surgery and the Pinhole Surgical Technique. The fourth is the cost analysis, covering expenses for each approach, potential insurance coverage, and the long-term value of professional care.
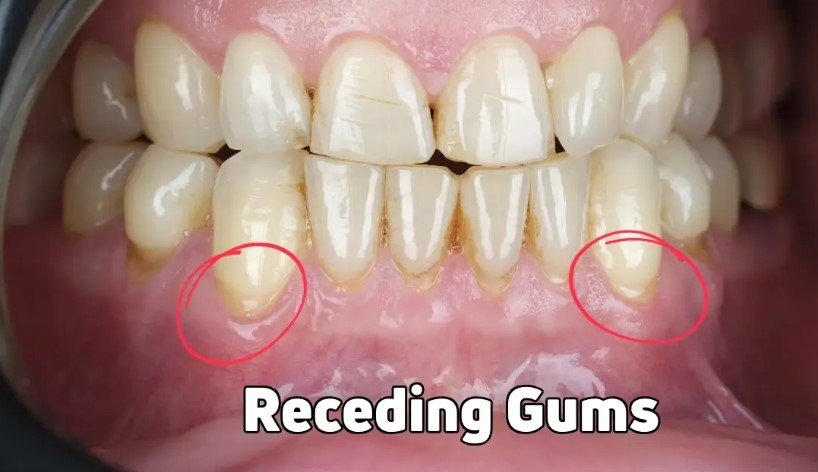
Receding gums, or gingival recession, is the process where the margin of the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away or pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This exposure creates gaps or “pockets” between the teeth and gum line, making it easy for disease-causing bacteria to build up. If left untreated, the supporting tissue and bone structures of the teeth can be severely damaged, potentially leading to tooth loss.
According to the American Dental Association (ADA), gum recession exposes tooth roots and increases sensitivity and decay risk.

Several factors contribute to gum recession. Identifying the cause is the first step in determining how to fix receding gums effectively.
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing with excessive force can physically wear away gum tissue over time. Conversely, poor oral hygiene allows plaque to harden into tartar, a hard substance that builds up on and between teeth and can only be removed by a dental professional, leading to inflammation and recession.
Periodontal disease (periodontitis) is the leading cause of gum recession. This bacterial infection destroys gum tissue and the supporting bone that holds your teeth in place. The recession is a visible symptom of this underlying disease. Research from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research shows untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis.
Smoking and tobacco use are significant risk factors, as they impair blood flow and healing in the gums. Genetic predisposition means some people are more susceptible to gum disease regardless of their care. Hormonal changes, particularly in women during pregnancy or menopause, can also make gums more sensitive and vulnerable.
Mayo Clinic explains that periodontal disease is a leading cause of gum recession in adults.
There are 5 primary symptoms of gum recession. These are visibly longer teeth, increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet stimuli, a notch felt near the gum line, gums that appear red, swollen, or bleed easily, and persistent bad breath. Noticing any of these signs indicates it’s time to evaluate gum recession treatment options.
A dentist or periodontist diagnoses gum recession during a periodontal exam. They use a probe to measure the depth of the pockets around each tooth. Pockets deeper than 3 millimeters often indicate a problem. They will also check for exposed root surfaces, assess bone loss via X-rays, and review your medical history to identify contributing factors.
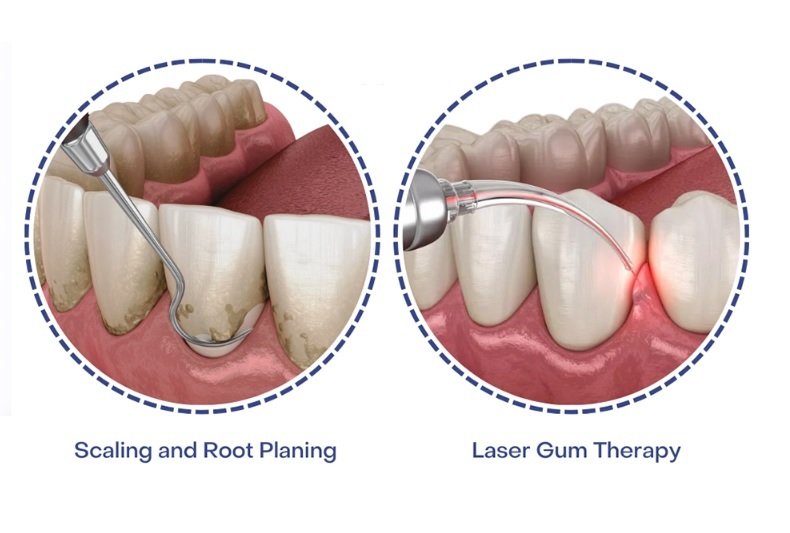
For mild to moderate recession, non-surgical treatments can halt the progression and improve gum health.
The foundational step to fix receding gums is correcting your home care. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush with gentle, circular motions. Floss daily to remove interproximal plaque. While antiseptic mouthwash can help reduce bacteria, it is not a substitute for mechanical plaque removal.
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure. Your dental professional removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gum line (scaling) and then smooths the tooth root (planing) to help the gums reattach. This is often the first-line professional treatment for gum disease.
In some cases, dentists use laser technology to remove diseased tissue and bacteria with precision. This minimally invasive option can promote better healing and is often used in conjunction with scaling and root planing.
Clinical studies indexed on PubMed report reduced bacteria and faster healing with dental laser therapy.
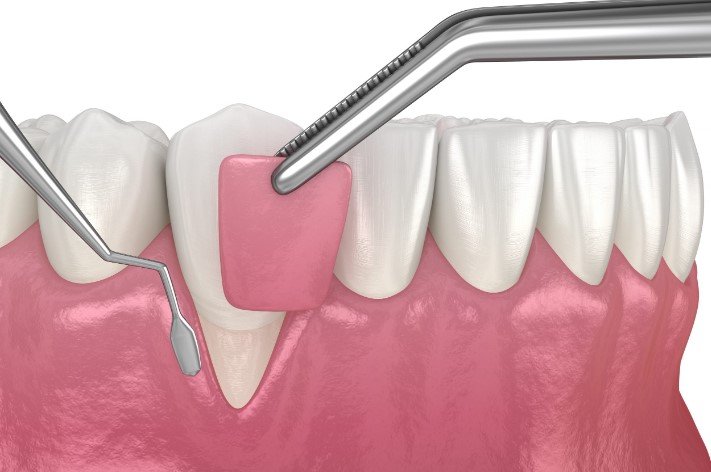
When recession is severe or non-surgical methods are insufficient, surgery is needed to restore the gum line.
Gum graft surgery involves taking tissue from another part of your mouth (usually the palate) or using donor tissue to cover exposed roots. The three main types are connective tissue grafts (most common), free gingival grafts (to add more gum tissue), and pedicle grafts (using adjacent gum). This procedure protects roots, reduces sensitivity, and stops further recession.
The Pinhole Surgical Technique (PST) is a minimally invasive alternative. A dentist makes a small hole in the existing gum tissue and uses special instruments to gently loosen and reposition the gum over the exposed root. It requires no sutures and typically offers faster recovery.
If the bone supporting your teeth has been destroyed, a regenerative procedure may be recommended. After folding back the gum tissue, your periodontist will place a regenerative material—like a membrane, graft tissue, or tissue-stimulating protein—to encourage your body to regenerate bone and tissue.

While these support overall gum health, they cannot reverse significant recession or replace professional treatment. Key supportive actions include eating a nutrient-rich diet with vitamin C, practicing oil pulling with coconut oil as a supplementary rinse, quitting smoking, and managing stress to reduce teeth grinding (bruxism).
Preventing gum recession hinges on consistent, proper care. There are 4 essential prevention strategies: brush gently twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush, floss daily, see your dentist for cleanings and check-ups every six months, and wear a nightguard if you grind your teeth.
Further Reading: 14 Natural Remedies for Receding Gums
The cost to fix receding gums varies dramatically based on the treatment type and severity, ranging from the low cost of home care to thousands of dollars for surgery. Understanding this range is central to evaluating receding gums treatment at home vs dentist cost.
Regarding comfort, modern dentistry prioritizes patient experience. Non-surgical cleanings involve minimal discomfort. Surgical procedures are performed under local anesthesia, and post-operative pain is manageable with medication.
A Comprehensive Dental Care practice provides a full continuum of treatment. They begin with an accurate diagnosis, create a personalized treatment plan that may progress from non-surgical treatments to surgical options, and offer long-term maintenance strategies. Their use of advanced imaging techniques and laser technology ensures precise, effective care.
No, receding gums cannot grow back naturally on their own. The gum tissue that has receded is lost permanently without professional intervention. However, procedures like gum graft surgery can effectively cover exposed roots and restore the gum line.
The timeline to fix receding gums ranges from a few weeks for non-surgical healing to 6-12 months for full surgical recovery. Non-surgical treatments like deep cleaning show improvement in weeks. Surgical graft healing takes 1-2 weeks for initial recovery, with final results stable after several months.
Modern treatments for receding gums are designed to be minimally uncomfortable. Procedures use local anesthesia. Post-treatment, any discomfort is usually mild and managed with over-the-counter pain relievers.
The cost to fix receding gums ranges from under $100 for preventive home care to over $3,000 per tooth for surgical grafting. The exact dentist cost depends on the procedure: deep cleaning averages $200-$800 per quadrant, while gum grafting averages $600-$3,000 per tooth.
Receding gums will not improve without intervention. Early action provides more affordable and less invasive treatment options. Schedule a consultation with a dental professional to get an accurate diagnosis and learn which treatment—from improved oral hygiene to gum graft surgery—is right for you.
Ignoring gum recession leads to worsened sensitivity, aesthetic concerns, and potential tooth loss. Investing in professional gum recession treatment protects your oral health, comfort, and smile. Contact a dentist to explore your personalized treatment plan and take the first step toward restoring your gum health.
Referral Links